Webscraper Tutorial
General Info
Automated-Jobs Dev Setup
- From the repository root, cd into the folder of the automated job you want to run (e.g., SEC, check-acq).
- Paste the env file into the corresponding automated job.
- Link to .env files (Need to be a paid OSU Sustainability Office Employee to see this link)
- Env files that are used by automated jobs will have a file name like "automated-jobs-XXXX.env.txt" (e.g. automated-jobs-pacific.env.txt for the pacific power scraper).
- Env files need
DASHBOARD_API = https://api.sustainability.oregonstate.edu/v2/energyunless you are making changes to energy dashboard (more on this in Testing Pipeline section)
- Ensure you are using the correct node version. Node version could potentially vary between automated jobs so refer to the README.md in folder of the automated job.
npm ito install packages.node <Javascript file name>, e.g.node readsec.jsto run webscraper.
AWS ECR (Elastic Container Registry)
AWS ECR is the registry that stores and versions the Docker images for each automated job. Any update to a webscraper gets pushed to ECR as an image, and ECS automatically runs the newest image.
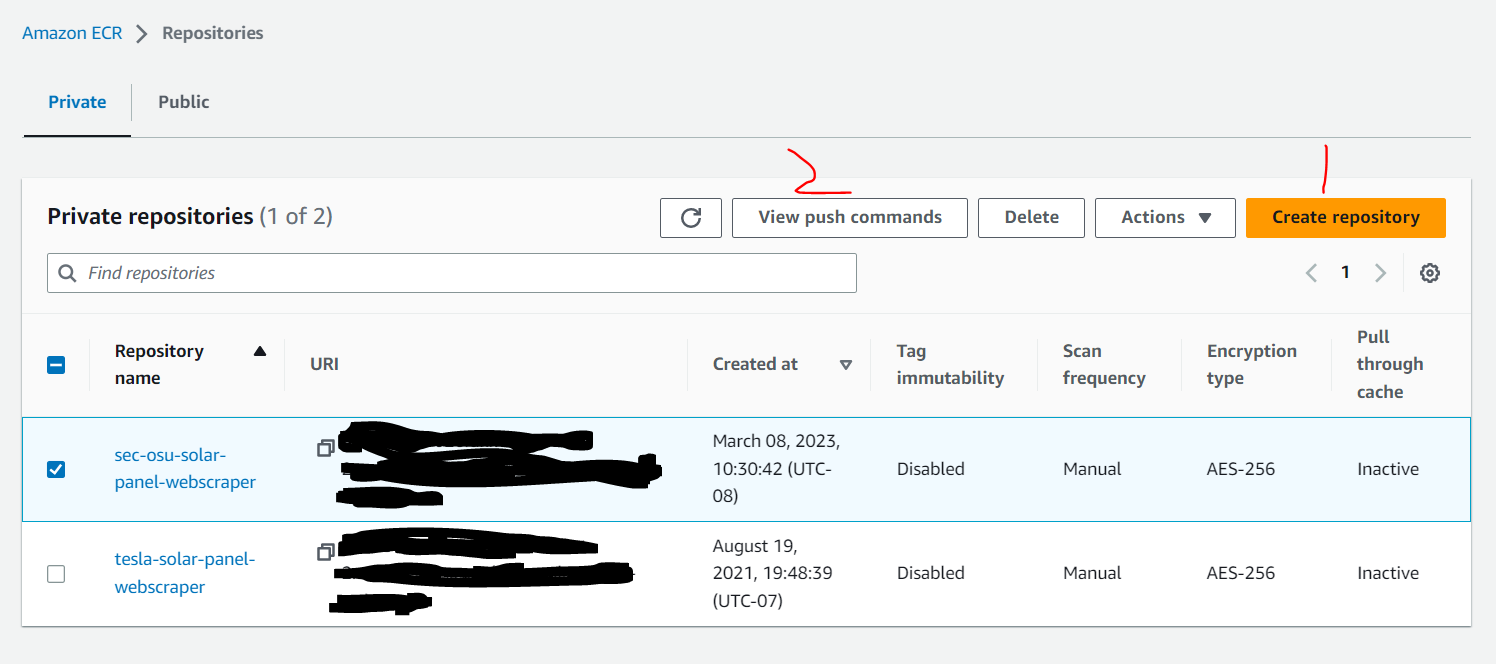
Creating a new repository
This is only necessary if a new automated job has been developed.
- Click "Create repository"
- In the "General settings" section, enter the repository name
- Leave everything else as-is and click "Create"
- Proceed to Creating a new task definition section
Pushing an image to an existing repository
Follow these steps when updating an existing automated job.
Prerequisites
- AWS CLI must be installed
- Docker Desktop App must be running in background
- For Windows Users:
- Windows PowerShell Admin
- If you are dealing with “execution of scripts is disabled on this system” issue, then this stack overflow article may be useful.
- Install the specific module for managing ECR through the AWS Tools for PowerShell using:
Install-AWSToolsModule AWS.Tools.ECR
- Windows PowerShell Admin
Steps
- From the AWS ECR Private repositories list, navigate to the desired automated job.
- Click "View push commands"
- Follow the AWS-provided push commands to authenticate, build, tag, and push your Docker image to the selected repository.
AWS ECS (Elastic Container Service)
AWS ECS is the service that runs the AWS ECR images as containers. ECS task definitions point to image URIs in ECR, so when you push an updated image to ECR, ECS can automatically pull and run the latest version.
Creating a new task definition
- From AWS ECS task definition page, click on "Create new task definition" > "Create new task definition" (not with JSON)
- Check the box for "AWS Fargate" as the launch type
- Leave Operating system/Architecture as-is
- We can typically use cheapest option for cpu/memory (0.25 vCPU/0.5 GB)
- In the Container details section, enter an appropriate container name.
- For Image URI, click "Browse ECR Images" > Your automated job ECR > "Use image tag: latest"
- In the logging section, enter the following values for each key:
- awslogs-group: /ecs/
- awslogs-region: us-west-2
- awslogs-stream-prefix: ecs
- awslogs-create-group: true
Note: If you are running into any issues, you can refer to an existing task definition's JSON configuration settings.
Creating a new cluster
- From AWS ECS cluster page, click "Create cluster"
- Use default options and click "Create"
- Go to the newly created cluster and click "Scheduled tasks"
- Click update on an existing scheduled task for reference before making a new one (have them side by side on different tabs!)
- While testing something for the first time, it's a good idea to set the interval for running the CRON job as something like every minute or every 5 minutes. But once you are certain it works, make sure to turn the interval back to once every 24 hours or 48 hours etc.
AWS Cloudwatch
AWS Cloudwatch log groups can be used for debugging purposes and to verify that the automated job has executed.
See this page on Cloudwatch as well for more information
Testing Pipeline Guide
Follow these steps in order to test your webscraper changes.
Step 1: Local Development Setup
Prerequisites:
- Ensure Node.js, Docker Desktop, and MySQL Workbench are installed
- Have access credentials for the SQL database and Energy Dashboard API
- Have the
.envfile for your automated job (e.g.,automated-jobs/SEC/.env) (Link to .env files)
Setup:
- Navigate to your automated job folder (e.g.,
automated-jobs/SEC/) - Install dependencies:
npm install - Ensure you're using the correct Node version (check the README.md in the folder)
Step 2: Local Testing (Node.js)
For webscraper-only changes:
- Edit the
DASHBOARD_APIvalue in your.envfile to use the production URL:DASHBOARD_API = https://api.sustainability.oregonstate.edu/v2/energy - Run the webscraper: (e.g.
node readsec.js) - Success criteria: New data appears in the SQL database via MySQL Workbench
For changes involving energy dashboard backend:
- Start the energy dashboard backend locally:
sam local start-api(should run on http://localhost:3000) - Edit the
DASHBOARD_APIvalue in your.envfile to use the local URL:DASHBOARD_API = http://localhost:3000 - Run the webscraper: (e.g. node readsec.js)
- Success criteria:
- New data appears in the SQL database
- Local frontend shows the data (check via Inspect Element > Network tab)
tip
API_PWDin your automated-jobs env file should match theAQUISUITE_PWDvalue that the energy-dashboard backend expects- Reference these files for backend integration details:
Step 3: Docker Testing
- Build the Docker image:
docker build . -t test - Run the Docker container:
docker run -t test - Success criteria:
- Container runs without errors
- New data appears in the SQL database
Step 4: AWS Deployment Testing
For webscraper updates only:
- You only need to push changes to ECR (not ECS)
- ECS should automatically pick up the latest ECR revision
Deployment steps:
- Push your Docker image to ECR
- Temporarily change the ECS scheduled task interval to 1 minute for testing:
- Go to ECS > cluster > scheduled task > update
- Set interval to 1 minute
- Monitor the deployment via Cloudwatch logs
- Important!! Once you see the run in CloudWatch logs, revert the scheduled task to its original interval
- Success criteria:
- Check Cloudwatch logs for successful execution
- Verify data appears on production sites:
- Confirm data in SQL database via MySQL Workbench
Step 5: Cleanup and Final Verification
Verify ECS interval: Confirm that the scheduled task has been reverted to its original interval
Remove duplicate data: If testing created duplicate entries, clean them up:
DELETE from Solar_Meters where id = <some id>info
Redundant data is handled on the frontend, but it's good practice to clean up
Final verification: Confirm everything works in production